
Supercharge Microsoft Power BI Development: How AI and TMDL Transform Your Workflow
Written by: Scott Davies, Business Intelligence Consultant at Climber.
In today’s fast-paced reporting environments, Microsoft Power BI developers are under constant pressure to deliver insights quickly and accurately. With the rise of AI tools, there’s now a smarter way to streamline your development workflow – and it starts with combining AI with the Tabular Model Definition Language (TMDL).
Accessing TMDL Viewer
In January 2025, Microsoft introduced the new TMDL view in Power BI. And as of September 2025, TMDL view is now generally available. Depending on the version of Power BI you are using, it may be necessary to enable this under Preview Features: click File, Options and Settings, Options, Preview features.
To access TMDL view, simply click the TMDL view button at the top left side of the screen.
TMDL view allows developers to generate a script which encapsulates the structure of the report. It’s possible to drag various elements of a report into the TMDL view, from specific tables, to measure the relationships between tables or even the entire semantic model. This generates a text-based description of the object(s) selected.
This is precisely what an AI engine needs to provide the necessary context when being asked to provide feedback on creating measures, or calculated columns, or reviewing the structure of a report.
When in TMDL view, on the right side of the screen is a pane for selecting from various elements of your report. Simply drag the required component(s) onto the screen of the TMDL view. The TMDL view has script pages as tabs along the bottom, allowing the creation of TMDL code for various aspects of your report.
Using AI to Understand Your Microsoft Power BI Model
So, by using a TMDL viewer, you can expose your model’s structure – including tables, columns, relationships, and measures – in a format that AI systems can easily interpret. This opens the door to using AI not just for ideation, but for actual development tasks.
It becomes a simple task to copy and paste the TMDL code into your AI system of choice. One caveat to be aware of is that, depending on what object(s) are being described, the TMDL view can become several thousand lines long. All AI systems will have limits in terms of how much data they can work with. These limits are much lower with free AI systems. However, my experience is that copying and pasting the TMDL view into notepad and uploading the resultant file provides a much wider scope for larger amounts of text and often remain within the limits of free AI services.
Claude Sonnet: A Strong Performer for Microsoft Power BI Tasks
At the time of writing, Claude Sonnet is showing excellent performance when working with TMDL inputs. However, I have found that Copilot with GPT-5 can give helpful results as well. With this being such a dynamic area, this situation will change day by day, so test out the systems you have access to, to work out which one works best for you.
Once you have your TMDL view data, you can use this in combination with a well-formed query to generate new DAX measures, suggest improvements, or even refactor existing logic. The results are often well-structured, readable, and ready to paste directly into your TMDL sheet.
“Please review the following TMDL file, which represents the semantic model of my Power BI report. I’d like you to analyse it and provide suggestions for improving the data model. Focus on areas such as:
- Table and column organisation
- Relationships and cardinality
- Naming conventions and consistency
- Use of calculated columns vs measures
- Performance optimisation opportunities
- Star schema design and granularity
- Any redundant or unused elements
Please explain your recommendations clearly and reference specific parts of the model where applicable.”
Generating DAX Measures with AI
One of the most practical use cases is generating DAX measures. Writing effective DAX measures can be troublesome, and even experienced Microsoft Power BI developers can sometimes struggle with this aspect. With the right prompt and context from your TMDL viewer, AI can:
- Create new measures based on business logic or KPIs
- Format them correctly for TMDL inclusion
- Include display folder assignments and formatting strings
This means you can go from idea to implementation in seconds – without switching between tools or manually formatting your code.
Creating a measure where you know what you need is one approach. However, what also works surprisingly well is to provide the AI system with the semantic model and ask it to generate measures that may be useful. This will not only create many measures you would have had to build one by one yourself, but also often creates measures you hadn’t considered, and which might prove extremely helpful.
“Using the TMDL definition, create appropriate measures in TMDL format (Indentation is important) that may be useful with this report, using the example below. Include a definition for each measure using /// to indicate a comment. When the measure is a number, format it with a thousand separator and no decimals. When it’s a percentage, format it as a percentage with 1 decimal place.
createOrReplace
ref table Orders
measure ‘Sales measure’ = sumx(Orders, Orders[Quantity]*Orders[UnitPrice])
lineageTag: 948d6cfe-89d8-44fa-87f1-79d1600b20b8
annotation PBI_FormatHint = {“isGeneralNumber”:true}”

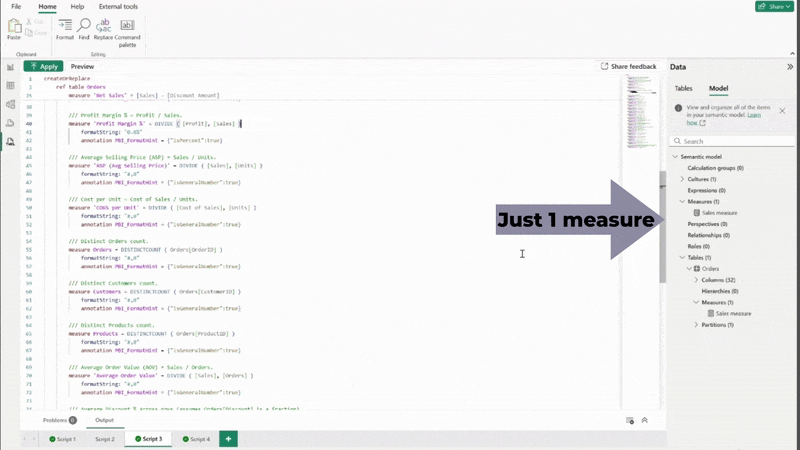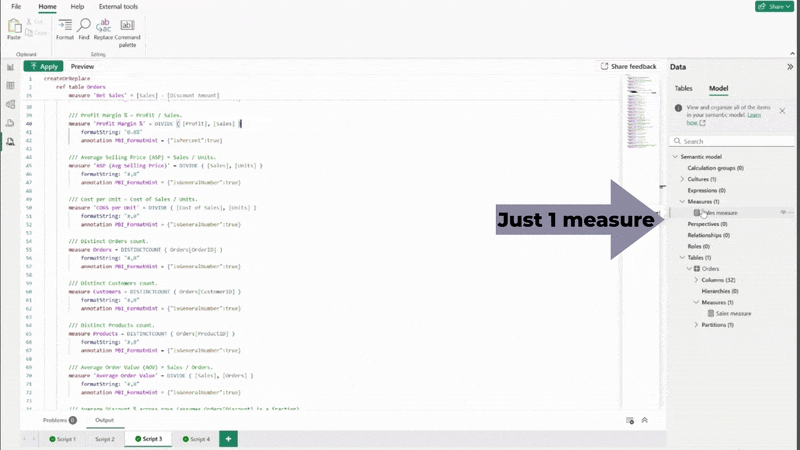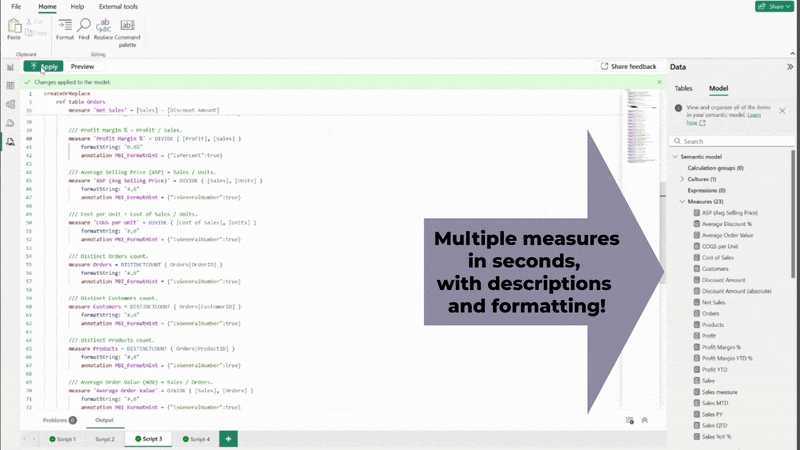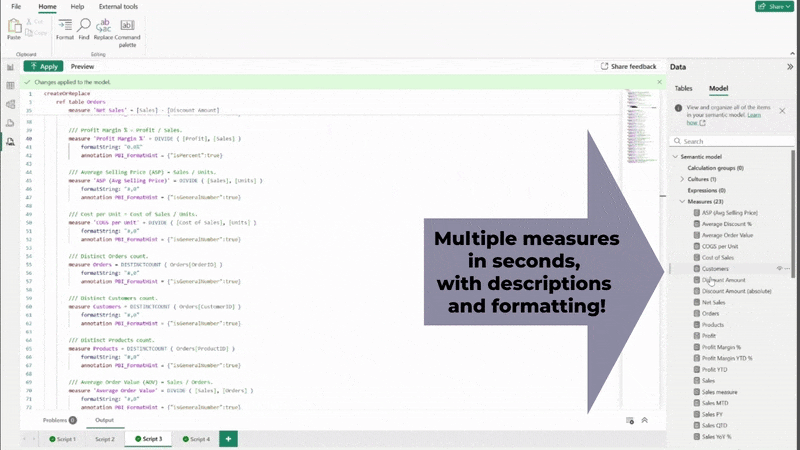
Copying the generated text, pasting this into a new TMDL script page, and clicking “Apply” creates multiple measures, formatted and described in a second. As always, remember to sense check the results of your AI system’s output.
Adding Descriptions and Metadata
Documentation is often overlooked in Microsoft Power BI projects, but it is essential for long-term maintainability. AI can help here too. By describing the purpose of a measure or column, your AI tool can generate concise, meaningful descriptions that can be added directly to your TMDL file, even on existing measures. This improves collaboration and makes your model easier to understand for future developers or stakeholders.
Conclusion
The TMDL view is ideal to provide the context that AI systems need. The combination provides scope for dramatic improvements in your reports and reductions in development timelines. Start experimenting with TMDL and AI today – your next Microsoft Power BI report could be your fastest yet!
WANT TO KNOW MORE? CONTACT US!
Scott Davies
BI Consultant & Training Manager
scott.davies@climberbi.co.uk
+44 203 858 0668
James Sharp
Managing Director
james.sharp@climberbi.co.uk
+44 203 858 0668
News archive

What’s New in Qlik Cloud – March 2026
An exciting update this month is Qlik’s new agentic experience in Qlik Cloud, delivered through Qlik Answers as a unified conversational interface. Qlik also continues to strengthen Qlik Talend Cloud across both architecture and day-to-day operations.
>> Read more
What’s New in Microsoft Fabric – February 2026
The February 2026 update of Microsoft Fabric delivered a mix of new capabilities now generally available (GA) and preview features across OneLake, real-time analytics, DevOps, SQL, and connectors.
>> Read more
Beyond QVDs: Building a Trusted Data Foundation with Qlik Talend Cloud
In this 40-minute webinar, you’ll learn why some organisations are rethinking QVD-centric architectures, what’s changed in the data landscape, and how Qlik Talend Cloud supports a trusted data foundation that becomes more cost effective and easier to operate over time.
>> Register now
